Every athlete trains to become bigger, faster and stronger. A large number of supplements have been created to help athletes achieve their goals. Among these supplements, one of the most important roles is assigned to BCAA amino acids. BCAAs or branch chained amino acids are branched-chain amino acids. There are only three of them: leucine, valine, and isoleucine. One of the main roles in this three belongs to leucine – it is he who provides the vast majority of the benefits that promises US the reception of BCAA. Why not take leucine separately? As it turned out, by itself, without the "support" of valine and isoleucine, leucine works much weaker. So we need all three branched-chain amino acids.

Basic properties of BCAA amino acids
- reduce seratonin production, thereby reducing mental fatigue and fatigue after exercise. It is seratonin that affects the feeling of fatigue.
- make up 1/3 of all amino acids in skeletal muscle
- the only amino acids that are metabolized primarily in skeletal muscle and to a much lesser extent in the liver.
- reduce the loss of other amino acids from the muscles during exercise and help the body absorb protein
- stimulate the production of insulin, which regulates blood sugar levels
- excellent anti-catabolic, help prevent the breakdown of muscle tissue, which is important for people on a strict diet
- they are stimulants of leptin synthesis. Leptin is a very interesting hormone that regulates metabolism, body weight, and appetite. Leptin secretion depends on the amount of fat in the body – the higher it is, the more leptin the body produces and Vice versa. When you go on a diet and lose fat, leptin secretion is reduced, which causes you to feel hungry. Leucine increases the secretion of leptin, that is, in a diet with its help, the feeling of hunger is blunted.
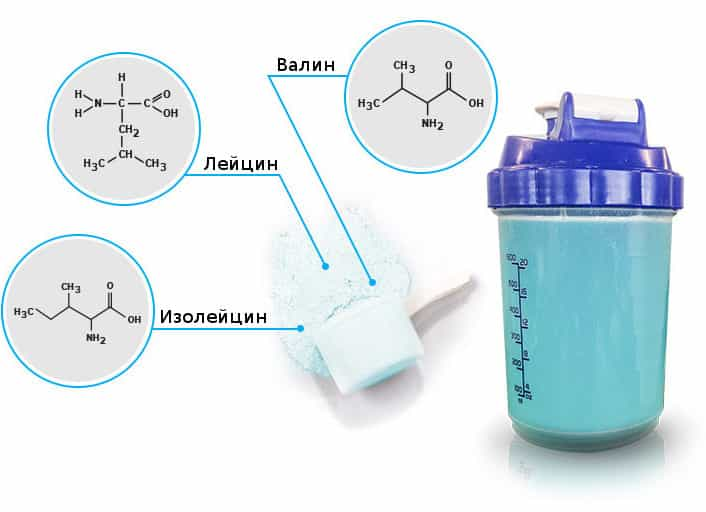 Leucine
Leucine
Leucine is one of three amino acids with branched side chains. This amino acid is the most important and frequently found in BCAA amino acid complexes. Less of it is found in whey protein concentrates. Since it became known that leucine increases the anabolic response of muscle cells to amino acids, athletes began to experiment with taking leucine supplements.
Leucine supplements help prevent massive muscle breakdown during a certain period of inactivity. The optimal dose of leucine is controversial, but it may well be high. Tests on animals showed that supplementation with leucine not only stimulates the growth of muscle tissue but also enhance the synthesis of collagen. Leucine can also help strengthen joints. Epidemiological studies show that the level is high.
Valine
Valine is an aliphatic amino acid with a non-polar character. It is closely related to leucine and isoleucine, with which it has a number of properties in common. These hydrophobic substances rarely take part in biochemical reactions, but they play a crucial role in determining the three-dimensional structure of proteins. In addition, valine promotes the absorption of other amino acids. Prevents muscle damage and supplies the tissues with extra glucose needed for energy production during physical activity. In combination with isoleucine and leucine, it promotes normal growth, tissue repair, regulates blood sugar levels, and provides the body with energy.
This essential amino acid is important for the Central and autonomic nervous system, is important for the adequate flow of cognitive functions, and is necessary for the proper functioning of the psyche. In addition, it is a substance that inhibits the transport of tryptophan.
Isoleucine
One of the main functions of isoleucine is the production of proteins. This means that the amino acid is the base material for proteins. The significance of this amino acid is already indicated by the fact that, together with leucine and valine, isoleucine makes up about 35 % of all muscle fiber in the body. This amino acid is a constant participant in the energy exchange process, including at the cell level. In addition, isoleucine protects the body from excessive serotonin production by restricting tryptophan access to brain cells.
How and when to take BCAA amino acids
Are there any side effects?
They are completely safe. When used in the recommended dosages, there are no side effects
1 reviews / Write a review






