WHAT IS CREATINE?
Creatine is a combination of three different amino acids: glycine, arginine, and methionine. By structure, creatine is nothing more than a combination of amino acids. Many people mistakenly refer creatine to pharmacology, this misconception is especially common among novice athletes! Creatine not only enters the body from outside, but is also produced by the body itself. Creatine is found in many types of meat, such as fish and red meat.
HOW DOES IT WORK?
After creatine enters the body (or after it is synthesized in the body) it first binds to a phosphate molecule to form creatine phosphate. ATP (adenosine triphosphate) is a universal source of energy for all biochemical processes occurring in living systems. When our body oxidizes carbohydrates, proteins, and fats, this is done in order to produce ATP. ATP belongs to the so-called macroergic compounds, that is, to chemical compounds containing bonds, during hydrolysis of which a significant amount of energy is released. Hydrolysis of macroergic bonds of the ATP molecule, accompanied by cleavage of 1 or 2 phosphoric acid residues, leads to the release, according to various data, from 40 to 60 kJ/mol.
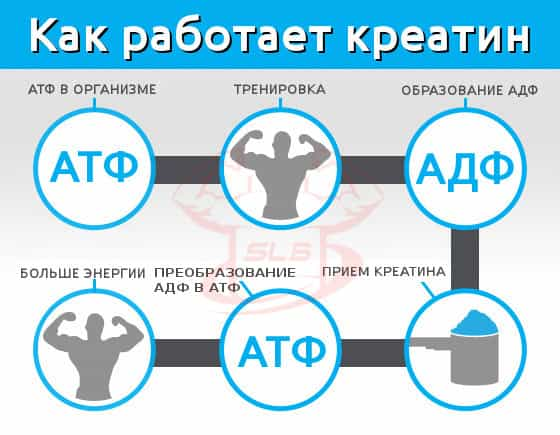
When the phosphate group is hydrolyzed, energy in the form of heat is released and this energy is used for various purposes, such as muscle contraction. After one phosphate has been lost from ATP, this compound is now converted to ADP (adenosine diphosphate). The reaction looks like this:
ATP + H2O → ADP + H3PO4 + energy
Now in the body have free ADP as a product from the hydrolysis of ATP. ADP is largely useless in the body unless it is converted back to ATP. This is where creatine comes into play. Phosphate-bound creatine donates its phosphate group to ADP, resulting in re-formed ATP!
Creatine phosphate + ADP → creatine + ATP
Thus, the main action of creatine is to maintain a constant concentration of ATP due to the reversible reaction of ATP re-phosphorylation from ADP and maintain the necessary reserves of ATP in muscle tissue. With constant heavy physical exertion, the level of creatine phosphate in muscle tissue can significantly decrease, which negatively affects the process of ATP resynthesis in the body. Accordingly, taking creatine can increase the level of creatine phosphate in muscle tissue.
In addition to regenerating ATP molecules, creatine phosphate is also known to neutralize acids that are formed during exercise and lower the pH of the blood, which causes muscle fatigue. Also, creatine monohydrate has the property of slightly retaining water in the muscle tissue, which leads to a slight increase in the weight of the athlete.
HOW SAFE IS IT?
 It should be noted that to date, there is not a single authoritative study proving that creatine has any dangerous side effects. This statement applies when used at a rate not exceeding the recommended dosage.
It should be noted that to date, there is not a single authoritative study proving that creatine has any dangerous side effects. This statement applies when used at a rate not exceeding the recommended dosage.
Possible, conditionally negative, side effects of creatine include: possible effects on the gastrointestinal tract(then creatine should be taken after a meal) and water retention, and as a result, weight gain.
However, note that you should not exceed the maximum daily creatine intake of 20 g, and you should not take creatine for more than 8 weeks.
DO I NEED TO CYCLE THE RECEPTION?
Taking a Supplement for more than 4-8 weeks is not advisable. And it's not about possible side effects, but about the return of creatine phosphate levels to normal. When we start taking creatine, the level of creatine phosphate in the body gradually increases, but the problem is that after a while the body tries to return its level to normal, as before taking a creatine Supplement. There is an opinion that the number of receptors that allow it to enter the cell decreases and the unclaimed one is removed from the body.
WHEN IS IT BETTER AND HOW TO TAKE IT?
Insulin helps to attract more creatine to the muscle cells, so take it with food that leads to the release of insulin into the blood, and this is primarily a food containing carbohydrates. Add it to a weight gainer or wash it down with a glass of juice. According to the time of reception - the most useful time will be after training.
DOES IT MAKE SENSE TO TAKE CREATINE BEFORE TRAINING?
You can take a pre-workout Supplement, but you won't benefit from it in the form of increased stamina and energy in this particular workout, before which you took creatine. As it was written above, the level of creatine phosphate increases gradually and you can notice the first results only a week after the start of taking it. In training, your body will use the creatine phosphate that is already in your cells, not the creatine that you just took.
0 reviews / Write a review
